In the early 1500s, Spain expanded its empire across the Atlantic Ocean. Spanish explorers and soldiers traveled to the Americas in search of land, wealth, and power. Many also wanted to spread Christianity to new peoples. These goals led Spain to explore and eventually conquer large areas of Central and South America.
The Spanish encountered two major civilizations: the Aztec Empire in present-day Mexico and the Inca Empire in the Andes Mountains of South America. These civilizations were powerful, wealthy, and highly organized. They built large cities, managed complex governments, and controlled rich natural resources, especially gold and silver. By conquering these empires, Spain gained direct access to that wealth, which became a major source of its power.
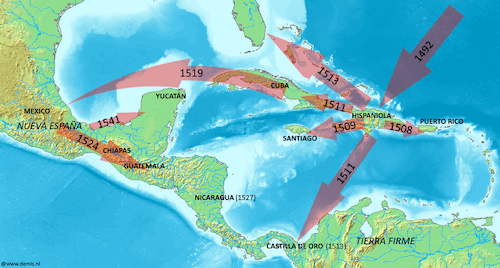
At first, Spanish explorers made contact with Indigenous leaders and learned about local customs. However, these early encounters often turned into efforts to take control. The Spanish used a combination of military force, surprise attacks, alliances with rival Indigenous groups, and strategic deception. Conquistadors also brought European diseases, such as smallpox and measles, which spread quickly through the region. These diseases caused widespread death and made it even harder for Indigenous peoples to resist the conquest.
After defeating the Aztec and Inca empires, Spain took control of large amounts of land and treasure. Ships loaded with gold and silver crossed the Atlantic, enriching the Spanish crown and increasing Spain’s power across Europe. This wealth was not only an effect of the conquest but also one of its driving causes.

The impact on Indigenous populations was severe. Millions of people died from disease, war, and forced labor. Indigenous governments, religions, and ways of life were disrupted or destroyed. Many Indigenous people were forced to convert to Christianity and follow Spanish laws and customs. While some cultural traditions survived, the daily lives of many communities were changed forever.
The conquest of Central and South America helped Spain become one of the most powerful empires in the world. By gaining control of advanced civilizations and their resources, Spain grew richer and stronger, but the human cost for the people who lived there first was enormous.
